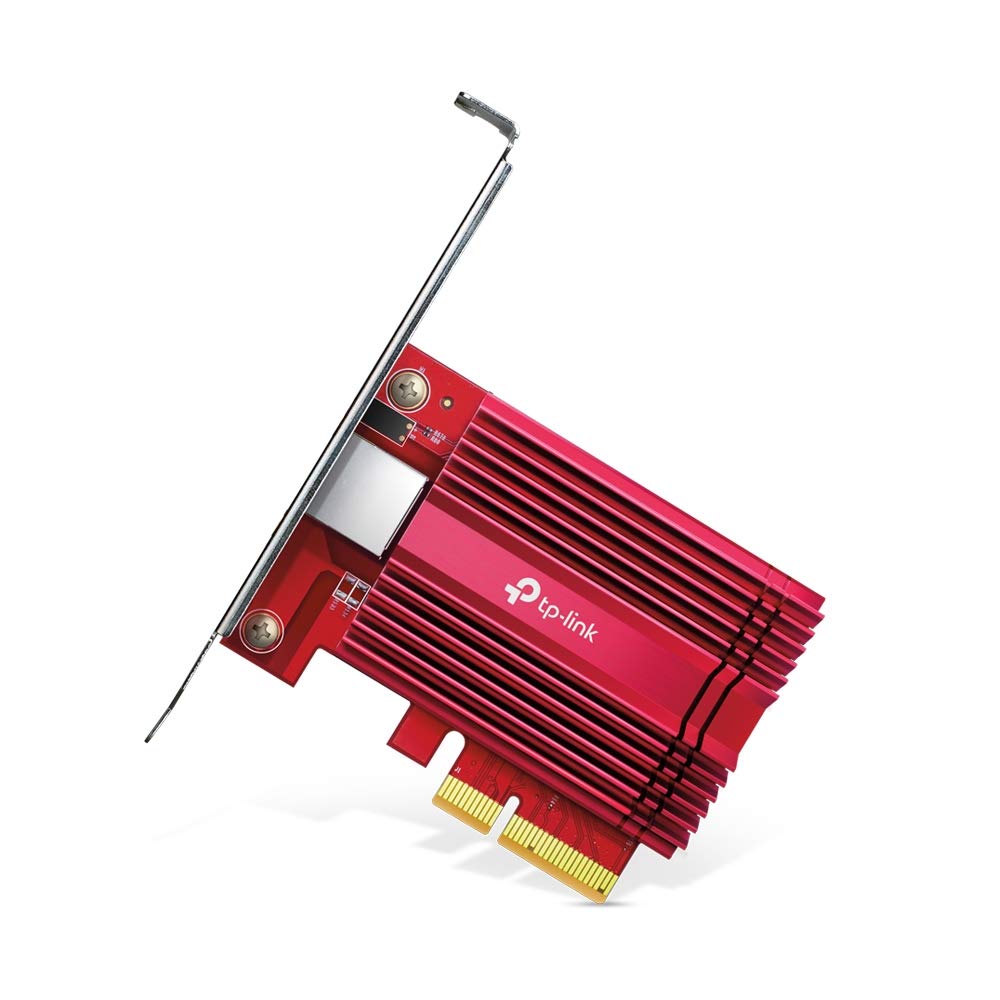
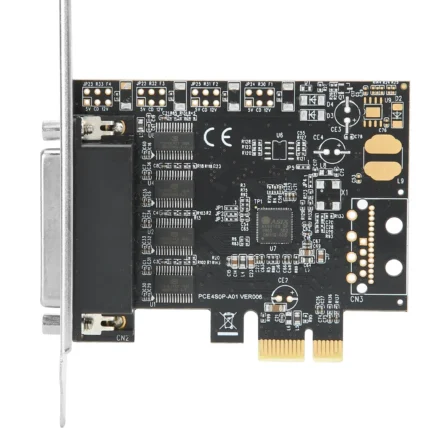
Network Card (LAN/Wi-Fi Adapter)
$39.00
A network card, also called a LAN card or Wi-Fi adapter, is a hardware component that enables a computer or device to connect to a wired or wireless network, allowing communication, file sharing, and internet access.
A Network Card, also known as a LAN card, Ethernet adapter, or Wi-Fi adapter, is a fundamental component in modern computing. It acts as a bridge between a computer and a network, allowing devices to communicate with each other, share resources, and access the internet. Without a network card, a computer would be limited to operating in isolation, unable to connect to the vast digital world that drives businesses, education, entertainment, and everyday communication.
1. Introduction to Network Cards
A network card is an interface that allows a computer to connect to a local area network (LAN) or a wireless network (Wi-Fi). It can be an internal component installed directly on the motherboard, or it can exist as an external device like a USB Wi-Fi adapter. Depending on the type of network connection required, the card may support wired Ethernet connectivity, wireless connections, or sometimes both.
When connected, the card translates data from the computer into signals that can be transmitted across the network medium—whether that’s copper cables, fiber optics, or radio waves in the case of Wi-Fi. Similarly, it also receives incoming signals and translates them back into data the computer can understand.
2. Types of Network Cards
There are several types of network cards available today, each designed for specific purposes:
Ethernet (LAN) Cards
These are wired network adapters that connect a computer to a network using an Ethernet cable (Cat5, Cat6, or higher).
They are known for reliability and stable speeds, often used in offices, gaming PCs, and servers.
Wireless Network Cards (Wi-Fi Adapters)
These adapters allow devices to connect to networks wirelessly using radio signals.
They are common in laptops, smartphones, and tablets, offering mobility and convenience without the need for cables.
Combo Cards
Many modern devices come with combo network cards that support both Ethernet and Wi-Fi connections.
These offer flexibility, ensuring users can switch between wired and wireless networks.
External USB Adapters
Portable solutions that plug into USB ports to provide Wi-Fi or LAN connectivity.
Useful when the internal network card is faulty or lacks modern standards (like Wi-Fi 6).
3. Key Functions of a Network Card
A network card performs several critical functions in ensuring seamless communication between devices:
Data Transmission: Converts digital data into electrical, optical, or radio signals.
Data Reception: Interprets signals from the network into usable data for the computer.
Unique Addressing: Provides a MAC address (Media Access Control address), a unique identifier for every network device.
Error Detection: Ensures data packets are transmitted correctly, with error-checking mechanisms.
Speed Negotiation: Adjusts to the available network speed, whether it’s 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, 1 Gbps, or even 10 Gbps.
4. Importance of Network Cards in Computing
In today’s interconnected world, network cards are essential. Here’s why they matter:
Internet Access: They enable browsing, streaming, video calls, and online gaming.
File Sharing: Allow computers to share documents, images, and media across a network.
Remote Work: Essential for connecting to cloud services and collaboration tools like Zoom, Teams, or Google Workspace.
Business Networking: In offices, LAN cards connect workstations to servers, printers, and storage systems.
Smart Homes: Wi-Fi adapters connect smart TVs, IoT devices, and appliances to the internet.
5. Evolution of Network Cards
Network cards have evolved dramatically over the years:
Early Ethernet Cards (1980s–1990s): Large add-on cards that supported only 10 Mbps speeds.
Fast Ethernet (1990s): Brought speeds up to 100 Mbps.
Gigabit Ethernet (2000s): Became the new standard, supporting 1 Gbps connections.
Wi-Fi Generations: From Wi-Fi 802.11b (11 Mbps) to the latest Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E, offering speeds in gigabits with reduced latency.
Integrated Network Interfaces: Today, most motherboards come with built-in LAN ports and Wi-Fi modules, reducing the need for separate cards.
6. Advantages of Network Cards
High-Speed Communication: Essential for fast downloads, video streaming, and gaming.
Reliable Connectivity: Wired LAN cards provide stable connections for critical tasks.
Mobility: Wi-Fi cards allow freedom from cables, enabling wireless networking.
Scalability: Easy to upgrade to newer standards like Wi-Fi 6 or 10-Gigabit Ethernet with add-on cards.
Compatibility: Works with all major operating systems (Windows, macOS, Linux).
7. Challenges and Limitations
Despite their advantages, network cards can have certain drawbacks:
Signal Interference (Wi-Fi): Wireless adapters may face issues with walls, distance, and electronic interference.
Cable Management (LAN): Wired connections require cables, which can be inconvenient in large setups.
Obsolescence: Older network cards may not support modern high-speed standards.
Hardware Failures: A faulty network card can completely disable connectivity.
8. Modern Developments
The latest advancements in network cards are transforming connectivity:
Wi-Fi 6 / Wi-Fi 6E: Supports faster speeds, greater efficiency, and lower latency, making it ideal for gaming, streaming, and large file transfers.
5G Network Adapters: Some modern adapters support cellular 5G networks for ultra-fast mobile connectivity.
10-Gigabit Ethernet Cards: Used in data centers and professional environments where ultra-high-speed wired connections are necessary.
Bluetooth Integration: Many Wi-Fi adapters now come with built-in Bluetooth for connecting wireless peripherals.
9. Real-World Applications
Home Use: Streaming Netflix, gaming online, browsing social media.
Business Use: Connecting workstations to office networks, secure file transfers, VoIP communication.
Education: Enabling remote learning, video lectures, and access to online resources.
Healthcare: Connecting hospital systems, IoT medical devices, and patient monitoring equipment.
Entertainment & Gaming: Low-latency Wi-Fi cards are critical for smooth online gaming experiences.
10. Conclusion
The Network Card (LAN/Wi-Fi Adapter) is a silent yet indispensable component of modern computing. From enabling high-speed wired connections to providing wireless freedom, it ensures that computers and devices remain interconnected in a global digital network. As technology advances, network cards continue to evolve, offering faster speeds, more reliable connections, and integration with emerging technologies like 5G and IoT.
Whether you’re streaming a movie, attending a virtual meeting, playing an online game, or managing a corporate data center, the network card is the unsung hero making it all possible. It is more than just a piece of hardware—it is the gateway to the digital world.
Fast Dispatch – Orders are processed within 24–48 hours after confirmation.
Secure Packaging – All products are packed safely to avoid damage during shipping.
Estimated Delivery – Standard delivery usually takes 3–7 business days depending on your location.
Tracking Available – Once your order is shipped, you’ll receive a tracking link via email/SMS.










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.